关于Muduo库
Muduo库简介 Muduo 是一个高性能的C++网络库,由陈硕(Giant Chen)开发并开源。它主要用于构建多线程的TCP网络服务程序,特别适合于高并发、低延迟的应用场景。Muduo的设计理念是简单、高效和易于使用,专注于提供可靠的网络通信功能,同时避免过度设计
Ubuntu下安装和使用Muduo库 首先,在Github上克隆Muduo库:
Bash git clone https://github.com/chenshuo/muduo.git
接着,进入Muduo库的根目录,然后执行以下命令进行编译和安装:
等待一段时间后,再执行下面的命令生成静态库:
此时,会在当前与克隆库的同一级显示build目录:
Text Only drwxrwxr-x 4 epsda epsda 4096 4月 14 20:15 build/
drwxrwxr-x 8 epsda epsda 4096 4月 14 20:15 muduo/
此时,在build目录中的release-install-cpp11/目录就包含了后续要使用到的头文件和静态库文件。而为了避免每次编译时都写上完整的路径,可以考虑在项目路径中添加两个软链接分别指向release-install-cpp11/include和release-install-cpp11/lib目录,例如
Bash ln -s /home/epsda/dependencies/build/release-install-cpp11/include/
ln -s /home/epsda/dependencies/build/release-install-cpp11/lib/
而因为是静态库,所以还需要带上-lmuduo_net和-lmuduo_base,这两个静态库是后续主要使用的库,其他的库暂不考虑
核心特点 事件驱动模型 :Muduo基于Reactor模式实现,使用epoll(Linux系统调用)作为底层事件通知机制。它通过事件循环(EventLoop)来处理I/O事件,能够高效地管理多个连接多线程支持 :Muduo采用「一个线程一个EventLoop」的设计,主线程负责监听新连接,工作线程池负责处理已建立的连接。这种设计避免了复杂的锁操作,减少了线程间的竞争,提升了性能非阻塞I/O :所有网络操作都是非阻塞的,确保了高并发场景下的性能跨平台性 :虽然Muduo主要针对Linux平台优化,但其代码结构清晰,理论上可以移植到其他支持类似I/O多路复用机制的平台上轻量级设计 :Muduo不依赖于任何第三方库(如Boost),仅依赖于标准C++库和POSIX API。它专注于核心网络功能,不包含额外的功能(如HTTP解析、序列化等),这使得它更加灵活和高效回调机制 :Muduo使用回调函数来处理事件(如连接建立、数据到达、连接关闭等),用户可以通过注册回调函数来定义自己的业务逻辑线程安全 :Muduo对线程安全进行了精心设计,确保在多线程环境下的正确性和高效性 一个线程一个EventLoop
「一个线程一个EventLoop」是一种在并发编程和异步I/O场景中广泛使用的设计模式。EventLoop(事件循环)是一个不断循环运行的程序结构,它的主要工作是不断地从事件队列中取出事件,并根据事件的类型调用相应的处理函数。在「一个线程一个EventLoop」模式下,每个线程都会独立运行一个 EventLoop。每个EventLoop负责处理该线程所关联的事件,例如网络I/O事件、定时器事件等。这种模式可以避免多线程之间的复杂同步问题,提高程序的并发性能和可维护性
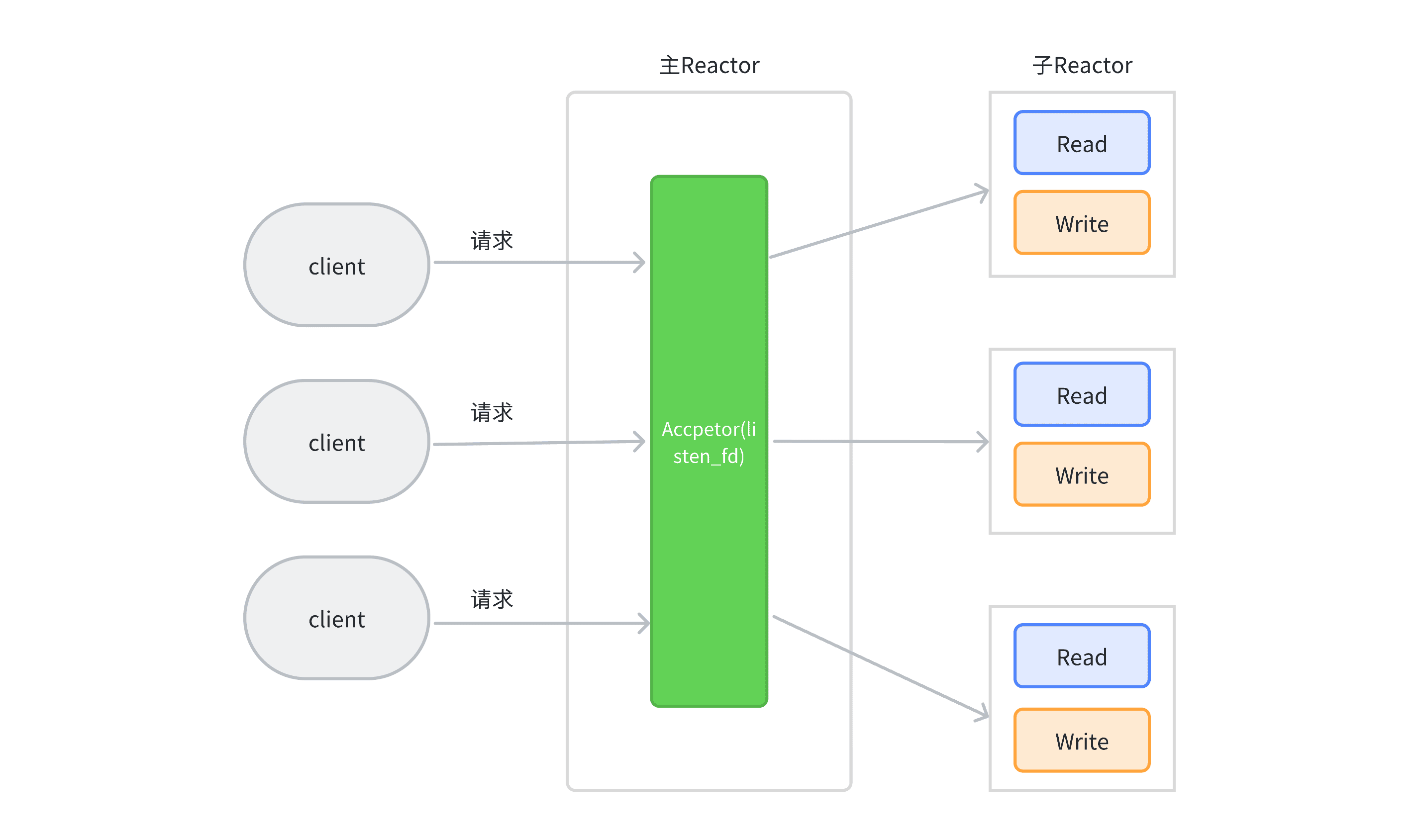
在网络服务器中,「一个线程一个EventLoop」可以理解为⼀个⽂件描述符只能由⼀个线程进⾏读写,换句话说就是⼀个TCP连接必须归属于某个EventLoop管理,示意图如下:
主要组件介绍 EventLoopEventLoop实例TcpServerTcpClientTcpConnectionBufferCountDownLatchCountDownLatch类进⾏同步控制 下面就常见的组件进行介绍
TcpServer类和EventLoop类前面已经知道了Muduo库设计的核心思想是「一个线程一个EventLoop」,那么在创建服务器时,本次以TCP为例,首先需要的就是TcpServer类,该类的作用就是创建一个TCP服务器,但是这个服务器本身并不进行阻塞等待连接,而是利用到epoll模型关心监听套接字的方式来完成对客户端的连接,所以除了需要TcpServer类之外,还需要一个EventLoop类作为服务器处理连接请求的核心。所以下面先来了解TcpServer类和EventLoop类
首先是TcpServer类,本次主要关心一部分后面重点使用的接口,代码如下:
TcpServer类 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class TcpServer : noncopyable
{
public :
enum Option
{
kNoReusePort ,
kReusePort ,
};
TcpServer ( EventLoop * loop ,
const InetAddress & listenAddr ,
const string & nameArg ,
Option option = kNoReusePort );
void setThreadNum ( int numThreads );
void start ();
/// 当⼀个新连接建⽴成功的时候被调⽤
void setConnectionCallback ( const ConnectionCallback & cb )
{ connectionCallback_ = cb ; }
/// 消息的业务处理回调函数---这是收到新连接消息的时候被调⽤的函数
void setMessageCallback ( const MessageCallback & cb ) { messageCallback_ = cb ; }
};
首先,该类继承了一个noncopyable类,该类的作用就是禁止该类的对象被拷贝,具体实现思想可以参考UDP编程接口基本使用 一节的介绍,此处不再提及
接着是创建对象的构造函数,正如前面提到的思路,Muduo库中的TcpServer本身不进行阻塞监听等待,而是利用epoll模型关心监听套接字,所以需要传递一个EventLoop类的对象地址作为其中的一个初始化参数,而在适当的时机就需要通过该对象启动EventLoop开始进行事件关心
然后是InetAddress类对象,这个对象在TcpServer类中表示当前服务器的地址和端口信息,其原型如下:
C++ class InetAddress : public muduo :: copyable
{
public :
InetAddress ( StringArg ip , uint16_t port , bool ipv6 = false );
};
其中第一个参数就是IP地址,第二个参数表示端口号,第三个参数表示是否使用IPv6地址,默认是不启用IPv6地址,所以是IPv4地址
回到TcpServer类的构造函数,接着是后两个参数,第一个表示当前服务器的名称,第二个表示是否开启地址重用,默认也是不开启,如果需要开启,只需要传递参数为Option枚举中的kReusePort即可
介绍完构造函数之后,接下来看常见的四个函数:
setThreadNum:这个函数表示设置当前服务器内部线程池中线程的个数,如果不设置,那么默认就是主线程负责获取新连接+IO处理,否则就是主线程的epoll模型处理获取新连接,新线程的epoll处理IOstart:这个函数表示启动服务器,但是需要注意的是,这个函数内部不会启动EventLoop开启事件关心,可以理解为就是创建套接字、绑定、开启监听以及设置一个标记位标识当前服务器启动,对应的启动EventLoop需要单独调用EventLoop类中的接口来完成。基于这个原因,需要先启动服务器再启动事件循环,否则先启动循环就无法正常启动服务器setConnectionCallback:这个函数表示在指定的连接状态(连接成功或者连接失败)时需要做出的行为,具体的行为由回调函数来决定setMessageCallback:这个函数表示在客户端给服务端发送信息时需要做出的行为,具体的行为也由回调函数来决定 对于前两个函数,上面已经介绍得差不多了,下面主要看后两个函数:setConnectionCallback和setMessageCallback
首先是setConnectionCallback,这个函数的参数是一个ConnectionCallback类型的函数对象,具体定义如下:
C++ typedef std :: function < void ( const TcpConnectionPtr & ) > ConnectionCallback ;
而TcpConnectionPtr表示一个TCP连接结构对象的指针,其原型如下:
C++ typedef std :: shared_ptr < TcpConnection > TcpConnectionPtr ;
接着是setMessageCallback,这个函数的参数是一个MessageCallback类型的函数对象,具体定义如下:
C++ typedef std :: function < void ( const TcpConnectionPtr & , Buffer * , Timestamp ) > MessageCallback ;
第一个参数与上面ConnectionCallback的参数相同,第二个参数表示缓冲区类对象指针,第三个表示一个时间戳,本次不考虑第三个参数,只考虑前两个参数
接着是EventLoop类,其原型如下:
EventLoop类 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class EventLoop : noncopyable
{
public :
/// Loops forever.
/// Must be called in the same thread as creation of the object.
void loop ();
/// Quits loop.
/// This is not 100% thread safe, if you call through a raw pointer,
/// better to call through shared_ptr<EventLoop> for 100% safety.
void quit ();
TimerId runAt ( Timestamp time , TimerCallback cb );
/// Runs callback after @c delay seconds.
/// Safe to call from other threads.
TimerId runAfter ( double delay , TimerCallback cb );
/// Runs callback every @c interval seconds.
/// Safe to call from other threads.
TimerId runEvery ( double interval , TimerCallback cb );
/// Cancels the timer.
/// Safe to call from other threads.
void cancel ( TimerId timerId );
};
在EventLoop类中,最核心的函数就是void loop();,其用于启动EventLoop,而对应地还有void quit();接口表示退出,其他接口介绍如下:
runAt:表示在指定的时间点 执行指定的任务runAfter:表示在指定的时间之后 执行指定的任务runEvery:表示每隔指定的时间 执行指定的任务cancel:表示停止指定的定时器 了解完TcpServer类和EventLoop类后,接下来需要了解TcpConnection和Buffer类
TcpConnection类该类用于描述每一个连接,其原型如下:
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41 class TcpConnection : noncopyable , public std :: enable_shared_from_this < TcpConnection >
{
public :
/// Constructs a TcpConnection with a connected sockfd
///
/// User should not create this object.
TcpConnection ( EventLoop * loop ,
const string & name ,
int sockfd ,
const InetAddress & localAddr ,
const InetAddress & peerAddr );
bool connected () const
{ return state_ == kConnected ; }
bool disconnected () const
{ return state_ == kDisconnected ; }
void send ( string && message ); // C++11
void send ( const void * message , int len );
void send ( const StringPiece & message );
// void send(Buffer&& message); // C++11
void send ( Buffer * message ); // this one will swap data
void shutdown (); // NOT thread safe, no simultaneous calling
void setContext ( const boost :: any & context )
{ context_ = context ; }
const boost :: any & getContext () const
{ return context_ ; }
boost :: any * getMutableContext ()
{ return & context_ ; }
void setConnectionCallback ( const ConnectionCallback & cb )
{ connectionCallback_ = cb ; }
void setMessageCallback ( const MessageCallback & cb )
{ messageCallback_ = cb ; }
private :
enum StateE
{
kDisconnected ,
kConnecting ,
kConnected ,
kDisconnecting
};
};
首先,该类除了继承了一个noncopyable类以外,还继承了enable_shared_from_this类,这个类在C++智能指针 部分介绍,此处不具体描述
本次主要考虑下面几个函数:
connected:表示服务端和客户端是否成功建立连接(可以开始接收和发送信息)disconnected:表示服务端和客户端是否断开建立连接send:表示发送数据的接口,具体使用哪一种版本会在具体场景中具体介绍shutdown:表示关闭当前连接 Buffer类这个类主要表示用于保存发送和接受数据的一个缓冲区,也就是说将来不论是客户端还是服务端,接收和发送的信息都存储在这个类的对象中,该类定义如下:
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57 class Buffer {
public :
static const size_t kCheapPrepend = 8 ;
static const size_t kInitialSize = 1024 ;
explicit Buffer ( size_t initialSize = kInitialSize )
: buffer_ ( kCheapPrepend + initialSize ), readerIndex_ ( kCheapPrepend ), writerIndex_ ( kCheapPrepend ) {}
void swap ( Buffer & rhs );
size_t readableBytes () const ;
size_t writableBytes () const ;
const char * peek () const ;
const char * findEOL () const ;
const char * findEOL ( const char * start ) const ;
void retrieve ( size_t len );
void retrieveInt64 ();
void retrieveInt32 ();
void retrieveInt16 ();
void retrieveInt8 ();
std :: string retrieveAllAsString ();
std :: string retrieveAsString ( size_t len );
void append ( const StringPiece & str );
void append ( const char * /*restrict*/ data , size_t len );
void append ( const void * /*restrict*/ data , size_t len );
char * beginWrite ();
const char * beginWrite () const ;
void hasWritten ( size_t len );
void appendInt64 ( int64_t x );
void appendInt32 ( int32_t x );
void appendInt16 ( int16_t x );
void appendInt8 ( int8_t x );
int64_t readInt64 ();
int32_t readInt32 ();
int16_t readInt16 ();
int8_t readInt8 ();
int64_t peekInt64 () const ;
int32_t peekInt32 () const ;
int16_t peekInt16 () const ;
int8_t peekInt8 () const ;
void prependInt64 ( int64_t x );
void prependInt32 ( int32_t x );
void prependInt16 ( int16_t x );
void prependInt8 ( int8_t x );
void prepend ( const void * /*restrict*/ data , size_t len );
};
在该类中,主要关心下面的函数:
readableBytes:表示缓冲区可读数据(有效数据)的长度peek:获取可读数据区域的起始地址retrieveAllAsString:获取缓冲区所有的数据,并以string对象返回retrieveAsString:获取缓冲区指定长度的数据,并以string对象返回peekInt32:尝试获取缓冲区4个字节的数据,并进行网络字节序转换使其变为当前计算机可以读取的整型数据,但是不会从缓冲区删除该4字节数据 retrieveInt32:从缓冲区中删除4个字节的数据readInt32:尝试获取缓冲区4个字节的数据,并进行网络字节序转换使其变为当前计算机可以读取的整型数据,并且从缓冲区删除该4字节数据 其他的接口到具体使用到的时候再具体实践中使用时介绍,目前只需要了解上面的接口
TcpClient类有时除了需要服务器端以外,还需要提供客户端,而在Muduo库中也有创建TCP客户端的类,即TcpClient类,该类定义如下:
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 class TcpClient : noncopyable
{
public :
TcpClient ( EventLoop * loop , const InetAddress & serverAddr , const string & nameArg );
~ TcpClient (); // force out-line dtor, for std::unique_ptr members.
void connect (); //连接服务器
void disconnect (); //关闭连接
void stop ();
//获取客⼾端对应的通信连接Connection对象的接⼝,发起connect后,有可能还没有连接建⽴成功
TcpConnectionPtr connection () const
{
MutexLockGuard lock ( mutex_ );
return connection_ ;
}
/// 连接服务器成功时的回调函数
void setConnectionCallback ( ConnectionCallback cb )
{ connectionCallback_ = std :: move ( cb ); }
/// 收到服务器发送的消息时的回调函数
void setMessageCallback ( MessageCallback cb )
{ messageCallback_ = std :: move ( cb ); }
};
从该类的构造函数可以看到,Muduo库的TcpClient类在设计时也采用了多路转接,所以也需要一个EventLoop对象
接着看其中的函数:
connect:与服务器建立连接,需要注意,这个函数不是阻塞的 disconnect:与服务器断开连接stop:停止客户端connection:获取客户端的连接结构对象的地址setConnectionCallback:与TcpServer的setConnectionCallback类似setMessageCallback:与TcpServer的setMessageCallback类似 CountDownLatch类除了上面的类外,还需要关注一个类CountDownLatch,这个类主要是做计数同步操作的,比如一个场景:客户端发起请求与服务器端建立连接,但是可能由于服务器端没有及时获取到这个连接,这就导致客户端以为可以发送信息,但是实际上不能发送信息,所以此时就可以通过CountDownLatch类对这种情况进行控制,具体控制方式在接下来的示例会有介绍。下面先了解CountDownLatch类如何做同步的,该类定义如下:
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30 class CountDownLatch : noncopyable
{
public :
explicit CountDownLatch ( int count );
void wait ()
{
MutexLockGuard lock ( mutex_ );
while ( count_ > 0 )
{
condition_ . wait ();
}
}
void countDown ()
{
MutexLockGuard lock ( mutex_ );
-- count_ ;
if ( count_ == 0 )
{
condition_ . notifyAll ();
}
}
int getCount () const ;
private :
mutable MutexLock mutex_ ;
Condition condition_ GUARDED_BY ( mutex_ );
int count_ GUARDED_BY ( mutex_ );
};
通过该类的实现可以得出:如果计数器大于0,那么就等待,否则如果计数器等于0,那么就停止等待
使用实例:使用Muduo库实现一个简单网络词典 服务端 根据上面的介绍,可以考虑设计下面的服务端程序:
类设计 主函数
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79 namespace dictionary_server
{
using namespace muduo ;
// 基于TCP的字典服务器端
class DictionaryServer
{
public :
DictionaryServer ( uint16_t port )
: server_ ( loop_ . get (),
net :: InetAddress ( "0.0.0.0" , port ),
"dict_server" ,
net :: TcpServer :: kReusePort )
, loop_ ( std :: make_shared < net :: EventLoop > ()) // 一定要确保EventLoop对象先创建
{
// 初始化字典
dict_ . insert ({ "hello" , "你好" });
dict_ . insert ({ "apple" , "苹果" });
dict_ . insert ({ "banana" , "香蕉" });
dict_ . insert ({ "watermelon" , "西瓜" });
dict_ . insert ({ "orange" , "橘子" });
// 设置回调
// 1. 连接回调
server_ . setConnectionCallback ([ this ]( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con ) {
this -> connectionCallback ( con );
});
// 2. 消息回调
server_ . setMessageCallback ([ this ]( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con , net :: Buffer * buffer , Timestamp t ){
this -> messageCallback ( con , buffer , t );
});
}
// 启动服务器
void startServer ()
{
// 启动服务器
// 先启动服务器,再开始事件关心
// 具体原因见文档介绍
server_ . start ();
loop_ -> loop ();
}
private :
void connectionCallback ( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con )
{
// 本次实现:连接成功和断开连接进行提示
if ( con -> connected ())
std :: cout << "连接成功" << std :: endl ;
else if ( con -> disconnected ())
std :: cout << "断开连接" << std :: endl ;
}
void messageCallback ( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con , net :: Buffer * buffer , Timestamp t )
{
// 本次实现:根据客户端的输入查找哈希表获取到结果返回给客户端
// 1. 获取客户端的输入
std :: string input = buffer -> retrieveAllAsString ();
// 2. 查找哈希表
auto pos = dict_ . find ( input );
// 3. 不存在返回错误字符串
if ( pos == dict_ . end ())
{
con -> send ( "无法查找到指定单词" );
return ;
}
// 4. 存在返回value
con -> send ( pos -> second );
}
private :
std :: shared_ptr < net :: EventLoop > loop_ ; // 事件模型,先初始化
net :: TcpServer server_ ; // 服务器
std :: unordered_map < std :: string , std :: string > dict_ ;
};
}
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 int main ( int argc , char * argv [])
{
if ( argc != 2 )
{
std :: cout << argv [ 0 ] << " port" << std :: endl ;
return 1 ;
}
dictionary_server :: DictionaryServer server ( std :: stoi ( argv [ 1 ]));
server . startServer ();
return 0 ;
}
客户端 根据上面的介绍,可以考虑设计下面的客户端程序:
类设计 主函数
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76 namespace dictionary_client
{
using namespace muduo ;
class DictionaryClient
{
public :
DictionaryClient ( std :: string ip , uint16_t port )
// : loop_(std::make_shared<net::EventLoop>())
: loopThread_ ( std :: make_shared < net :: EventLoopThread > ())
, loop_ ( loopThread_ -> startLoop ())
, client_ ( loop_ . get (),
net :: InetAddress ( ip , port ),
"dict_client" )
, count_ ( 1 ) // 确保客户端在连接建立成功后发送消息
{
// 设置回调函数
// 1. 连接回调
client_ . setConnectionCallback ( std :: bind ( & DictionaryClient :: connectionCallback , this , std :: placeholders :: _1 ));
// 2. 消息回调
client_ . setMessageCallback ( std :: bind ( & DictionaryClient :: messgaeCallback , this , std :: placeholders :: _1 , std :: placeholders :: _2 , std :: placeholders :: _3 ));
client_ . connect ();
// 客户端开始在同步计数器等待,防止未连接时发送信息
count_ . wait ();
// 不能直接开始loop,一旦开始loop就无法调用send发送数据
// 定义EventLoopThread,让新线程自动开始事件关心
}
void send ( const std :: string & msg )
{
if ( con_ -> disconnected ())
{
std :: cout << "连接已断开" << std :: endl ;
return ;
}
con_ -> send ( msg );
}
private :
void connectionCallback ( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con )
{
if ( con -> connected ())
{
std :: cout << "客户端连接成功" << std :: endl ;
// 设置连接对象指针,便于接下来调用send
con_ = con ;
// 更改同步计数器,减到0表示成功连接,唤醒客户端,可以进行消息发送
count_ . countDown ();
}
else if ( con -> disconnected ())
{
std :: cout << "客户端断开连接" << std :: endl ;
// 重置连接指针
con_ . reset ();
}
}
void messgaeCallback ( const net :: TcpConnectionPtr & con , net :: Buffer * buffer , Timestamp t )
{
// 收到消息时才会执行,所以此处不能调用send
std :: string out = buffer -> retrieveAllAsString ();
std :: cout << out << std :: endl ;
}
private :
std :: shared_ptr < net :: EventLoopThread > loopThread_ ;
std :: shared_ptr < net :: EventLoop > loop_ ;
net :: TcpClient client_ ;
net :: TcpConnectionPtr con_ ; // 需要调用send接口
CountDownLatch count_ ;
};
}
C++ 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 int main ( int argc , char * argv [])
{
if ( argc != 2 )
{
std :: cout << argv [ 0 ] << " port" << std :: endl ;
return 1 ;
}
dictionary_client :: DictionaryClient client ( "127.0.0.1" , std :: stoi ( argv [ 1 ]));
while ( 1 )
{
std :: string msg ;
std :: cin >> msg ;
client . send ( msg );
}
return 0 ;
}
测试 使用下面的Makefile进行客户端和服务端编译:
Makefile all : server client
server : server .cc
g++ $^ -o $@ -I./include -L./lib -lmuduo_net -lmuduo_base -lpthread
client : client .cc
g++ $^ -o $@ -I./include -L./lib -lmuduo_net -lmuduo_base -lpthread
.PHONY : clean
clean :
rm -f server client
编译运行后即可发现可以正常通信